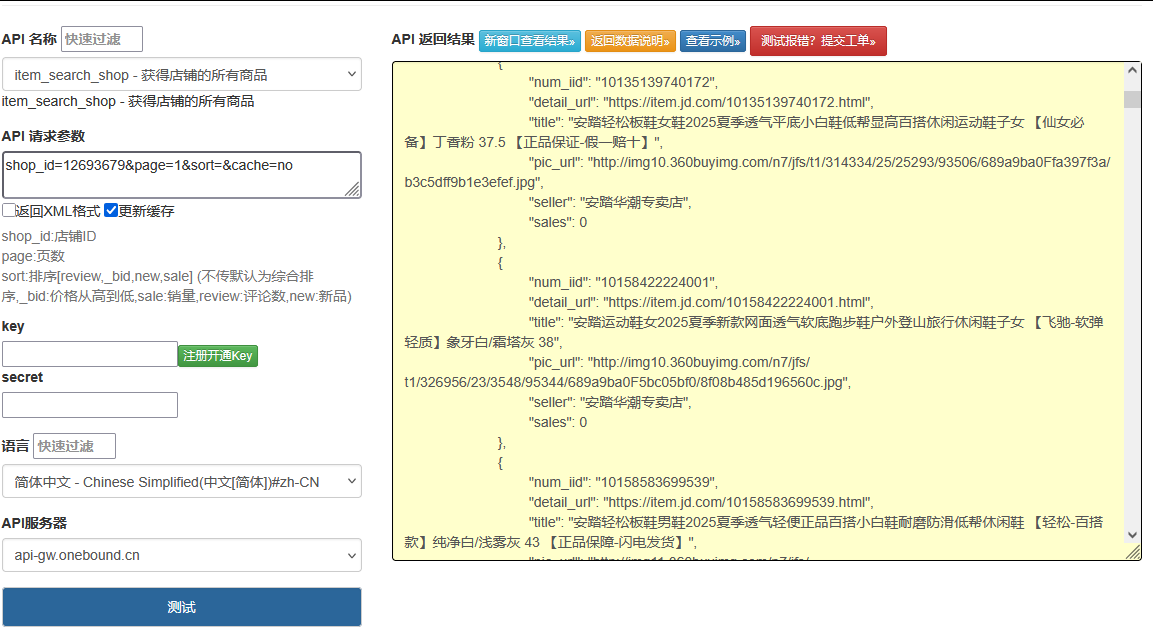
京东平台的店铺商品接口是获取商家全量商品信息的核心通道,相比单商品接口,它能批量获取店铺内所有商品的基础信息、价格、库存和促销状态,在店铺竞品分析、品类结构研究、价格监测等场景中具有重要应用价值。本文将聚焦京东店铺商品接口的批量采集技术,从接口权限申请、分页递归采集、数据去重清洗到品类结构可视化,结合完整代码实现,帮助开发者合规高效地获取店铺全量商品数据。
一、接口特性与核心数据结构
京东店铺商品接口(
jd.shop.item.list.get)具有鲜明的批量处理特性,主要特点包括:分页批量返回:支持按页获取店铺商品,单页最大 100 条
多维度筛选:可按商品状态、品类、价格区间等筛选
完整商品属性:包含基础信息、价格、库存、促销等核心字段
店铺关联数据:返回商品与店铺的关联信息,如是否主推商品
核心参数解析
| 参数类别 | 具体参数 | 作用说明 | 约束条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基础参数 | app_key | 应用标识 | 开放平台注册获取 |
method | 接口方法名 | 固定为jd.shop.item.list.get | |
timestamp | 时间戳 | 格式 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,误差≤5 分钟 | |
sign | 签名 | HMAC-SHA256 加密 | |
| 业务参数 | shop_id | 店铺 ID | 必选,京东店铺唯一标识 |
page | 页码 | 正整数,默认 1 | |
page_size | 每页条数 | 1-100,默认 20 | |
| 筛选参数 | item_status | 商品状态 | 0 - 全部,1 - 在售,2 - 下架 |
cid3 | 三级分类 ID | 可选,筛选指定分类商品 | |
price_from | 最低价格 | 可选,单位元 | |
price_to | 最高价格 | 可选,单位元 |
响应数据结构
接口返回数据包含商品列表和分页信息,核心结构如下:
json
{
"jd_shop_item_list_get_response": {
"result": {
"total": 856, // 店铺商品总数
"page": 1,
"page_size": 50,
"items": [
{
"sku_id": "100012345678", // 商品SKU ID
"spu_id": "1234567", // 商品SPU ID
"title": "XX品牌无线蓝牙耳机 主动降噪",
"brand_name": "XX品牌",
"cid1": 122, // 一级分类ID
"cid1_name": "数码",
"cid2": 1223, // 二级分类ID
"cid2_name": "耳机",
"cid3": 12234, // 三级分类ID
"cid3_name": "无线耳机",
"price": "299.00", // 价格
"market_price": "399.00", // 市场价
"stock": 1250, // 库存
"stock_state": 33, // 库存状态(33-有货)
"is_main": 1, // 是否为主推商品(1-是)
"is_hot": 0, // 是否为热销商品(0-否)
"create_time": "2024-05-15 09:30:00", // 上架时间
"update_time": "2024-08-10 14:20:30", // 更新时间
"sales_count": 3560, // 30天销量
"comment_count": 1250 // 评论数
}
// 更多商品...
]
}
}}二、开发环境与权限配置
环境要求
开发语言:Python 3.8+
核心依赖:
requests(HTTP 请求)、pandas(数据处理)、matplotlib(可视化)开发工具:PyCharm/VS Code
运行环境:支持 Windows/macOS/Linux,需联网访问京东开放平台
依赖安装
bash
pip install requests pandas matplotlib redis pycryptodome tqdm
店铺商品接口权限说明
京东店铺商品接口权限获取需注意:
个人开发者几乎无法获取,需企业认证账号
需明确说明使用场景,不得用于恶意爬取竞争店铺数据
调用限制严格:默认 30 次 / 分钟,单店铺日采集上限 1000 次
部分高销量店铺可能需要特殊权限申请
三、接口开发实战实现
步骤 1:基础工具与签名生成
python
运行
import timeimport hashlibimport hmacimport urllib.parseimport loggingfrom typing import Dict, Tuple# 配置日志logging.basicConfig(
filename='jd_shop_items.log',
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')def generate_jd_sign(params: Dict, app_secret: str) -> str:
"""生成京东接口签名(HMAC-SHA256)"""
sorted_params = sorted(params.items(), key=lambda x: x[0])
query_string = urllib.parse.urlencode(sorted_params)
signature = hmac.new(
app_secret.encode('utf-8'),
query_string.encode('utf-8'),
hashlib.sha256 ).hexdigest().upper()
return signaturedef validate_shop_item_params(params: Dict) -> Tuple[bool, str]:
"""验证店铺商品接口参数"""
required = ["shop_id", "page", "page_size"]
for param in required:
if param not in params:
return False, f"缺少必选参数: {param}"
# 验证分页参数
if not isinstance(params["page"], int) or params["page"] < 1:
return False, "page必须是正整数"
if not isinstance(params["page_size"], int) or not (1 <= params["page_size"] <= 100):
return False, "page_size必须是1-100的整数"
# 验证商品状态参数
if "item_status" in params and params["item_status"] not in [0, 1, 2]:
return False, "item_status必须是0-2的整数"
return True, "参数验证通过"步骤 2:店铺商品接口客户端
python
运行
import requestsimport jsonfrom typing import Dict, Optional, Anyclass JdShopItemAPI:
def __init__(self, app_key: str, app_secret: str):
self.app_key = app_key
self.app_secret = app_secret
self.api_url = "https://api.jd.com/routerjson"
def get_shop_items(self,
shop_id: str,
page: int = 1,
page_size: int = 50,
item_status: int = 1, # 默认获取在售商品
cid3: int = None,
price_from: float = None,
price_to: float = None) -> Optional[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
获取店铺商品列表
:param shop_id: 店铺ID
:param page: 页码
:param page_size: 每页条数
:param item_status: 商品状态 0-全部 1-在售 2-下架
:param cid3: 三级分类ID
:param price_from: 最低价格
:param price_to: 最高价格
:return: 商品列表数据
"""
# 构建业务参数
params = {
"shop_id": shop_id,
"page": page,
"page_size": page_size,
"item_status": item_status }
# 添加可选参数
if cid3:
params["cid3"] = cid3 if price_from is not None:
params["price_from"] = price_from if price_to is not None:
params["price_to"] = price_to
# 参数验证
valid, msg = validate_shop_item_params(params)
if not valid:
logging.error(f"参数错误: {msg}")
return None
# 构建完整请求参数
full_params = {
"method": "jd.shop.item.list.get",
"app_key": self.app_key,
"timestamp": time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"),
"format": "json",
"v": "2.0",** params }
# 生成签名
full_params["sign"] = generate_jd_sign(full_params, self.app_secret)
try:
# 发送请求
response = requests.post(
self.api_url,
data=full_params,
headers={"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"},
timeout=15
)
response.raise_for_status()
result = json.loads(response.text)
# 错误处理
if "error_response" in result:
error = result["error_response"]
logging.error(f"接口错误: {error.get('msg')} (错误码: {error.get('code')})")
return None
return result.get("jd_shop_item_list_get_response", {}).get("result", {})
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
logging.error(f"HTTP请求异常: {str(e)}")
return None
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
logging.error(f"JSON解析错误: {str(e)}")
return None步骤 3:全量商品数据采集器
python
运行
import timeimport pandas as pdfrom tqdm import tqdmfrom typing import Tuple, Optionalclass JdShopItemCrawler:
def __init__(self, api: JdShopItemAPI):
self.api = api
self.delay_seconds = 2 # 请求间隔,避免触发限流
self.max_retry = 3 # 单页最大重试次数
def crawl_shop_all_items(self,
shop_id: str,
item_status: int = 1,
max_items: int = None) -> Tuple[pd.DataFrame, Dict]:
"""
采集店铺所有商品
:param shop_id: 店铺ID
:param item_status: 商品状态
:param max_items: 最大采集数量,None表示采集全部
:return: 商品DataFrame和统计信息
"""
all_items = []
total_stats = None
page = 1
page_size = 100 # 单页最大数量,提高采集效率
# 获取第一页数据,确定总数量
first_page = self._get_with_retry(
shop_id=shop_id,
page=1,
page_size=page_size,
item_status=item_status )
if not first_page:
return pd.DataFrame(), {}
# 解析第一页数据
first_df, first_stats = self.parse_shop_items(first_page)
all_items.append(first_df)
total_stats = first_stats
# 计算需要采集的总页数
total_items = first_stats.get("total", 0)
if max_items and total_items > max_items:
total_items = max_items
total_pages = (total_items + page_size - 1) // page_size
if total_pages <= 1:
combined_df = pd.concat(all_items, ignore_index=True)
return (combined_df.iloc[:max_items] if max_items else combined_df), total_stats
# 采集剩余页数
for page in tqdm(range(2, total_pages + 1), desc=f"采集店铺 {shop_id} 商品"):
# 控制请求频率
time.sleep(self.delay_seconds)
# 获取当前页数据
page_data = self._get_with_retry(
shop_id=shop_id,
page=page,
page_size=page_size,
item_status=item_status )
if page_data:
page_df, _ = self.parse_shop_items(page_data)
all_items.append(page_df)
# 检查是否达到最大采集数量
if max_items and len(pd.concat(all_items, ignore_index=True)) >= max_items:
break
else:
logging.warning(f"第{page}页商品采集失败,跳过")
# 合并所有数据
combined_df = pd.concat(all_items, ignore_index=True)
# 截取最大数量
if max_items and len(combined_df) > max_items:
combined_df = combined_df.iloc[:max_items]
return combined_df, total_stats
def _get_with_retry(self, **kwargs) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""带重试机制的页面获取"""
for retry in range(self.max_retry):
data = self.api.get_shop_items(** kwargs)
if data:
return data
logging.warning(f"第{retry+1}次重试获取数据")
time.sleep(self.delay_seconds * (retry + 1)) # 指数退避
return None
@staticmethod
def parse_shop_items(raw_data: Dict) -> Tuple[pd.DataFrame, Dict]:
"""解析店铺商品数据"""
if not raw_data or "items" not in raw_data:
return pd.DataFrame(), {}
# 提取统计信息
stats = {
"total": raw_data.get("total", 0),
"page": raw_data.get("page", 1),
"page_size": raw_data.get("page_size", 20),
"total_pages": (raw_data.get("total", 0) + raw_data.get("page_size", 20) - 1)
// raw_data.get("page_size", 20)
}
# 解析商品列表
items = []
for item in raw_data["items"]:
item_info = {
"sku_id": item.get("sku_id"),
"spu_id": item.get("spu_id"),
"title": item.get("title"),
"brand_name": item.get("brand_name"),
"cid1": item.get("cid1"),
"cid1_name": item.get("cid1_name"),
"cid2": item.get("cid2"),
"cid2_name": item.get("cid2_name"),
"cid3": item.get("cid3"),
"cid3_name": item.get("cid3_name"),
"price": item.get("price"),
"market_price": item.get("market_price"),
"stock": item.get("stock"),
"stock_state": item.get("stock_state"),
"is_main": item.get("is_main", 0),
"is_hot": item.get("is_hot", 0),
"create_time": item.get("create_time"),
"update_time": item.get("update_time"),
"sales_count": item.get("sales_count", 0),
"comment_count": item.get("comment_count", 0)
}
items.append(item_info)
# 转换为DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(items)
# 数据类型转换
if not df.empty:
df["price"] = pd.to_numeric(df["price"], errors="coerce")
df["market_price"] = pd.to_numeric(df["market_price"], errors="coerce")
df["stock"] = pd.to_numeric(df["stock"], errors="coerce")
df["sales_count"] = pd.to_numeric(df["sales_count"], errors="coerce")
df["comment_count"] = pd.to_numeric(df["comment_count"], errors="coerce")
df["create_time"] = pd.to_datetime(df["create_time"], errors="coerce")
df["update_time"] = pd.to_datetime(df["update_time"], errors="coerce")
df["is_main"] = df["is_main"].astype(bool)
df["is_hot"] = df["is_hot"].astype(bool)
return df, stats步骤 4:商品数据清洗与去重
python
运行
import redef clean_shop_item_data(df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""清洗店铺商品数据"""
if df.empty:
return df
df_clean = df.copy()
# 1. 去重(根据sku_id去重)
df_clean = df_clean.drop_duplicates(subset=["sku_id"], keep="last")
# 2. 处理缺失值
# 填充价格缺失值(用市场价代替)
price_mask = df_clean["price"].isna() & ~df_clean["market_price"].isna()
df_clean.loc[price_mask, "price"] = df_clean.loc[price_mask, "market_price"]
# 填充品牌缺失值
df_clean["brand_name"] = df_clean["brand_name"].fillna("未知品牌")
# 3. 计算折扣率
def calculate_discount(row):
if pd.notna(row["price"]) and pd.notna(row["market_price"]) and row["market_price"] > 0:
return round(row["price"] / row["market_price"], 2)
return None
df_clean["discount_rate"] = df_clean.apply(calculate_discount, axis=1)
# 4. 提取商品标题关键词
def extract_title_keywords(title):
if not title:
return []
# 简单提取数字和品牌相关关键词
keywords = re.findall(r'(\d+[寸|英寸|g|kg|ml|L|W|H|mm|cm|m])', str(title))
# 提取品牌关键词
if df_clean["brand_name"].notna().any():
brand = row.get("brand_name", "")
if brand and brand != "未知品牌" and brand in str(title):
keywords.append(brand)
return list(set(keywords))
df_clean["title_keywords"] = df_clean.apply(
lambda row: extract_title_keywords(row["title"]), axis=1
)
# 5. 标记库存状态
df_clean["in_stock"] = df_clean["stock_state"] == 33
return df_clean步骤 5:店铺商品数据分析与可视化
python
运行
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport seaborn as snsfrom matplotlib.font_manager import FontPropertiesimport pandas as pd# 设置中文字体plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"]sns.set(font_scale=1.2)sns.set_style("whitegrid")def analyze_shop_category(df: pd.DataFrame) -> Tuple[Dict, pd.DataFrame]:
"""分析店铺品类结构"""
if df.empty:
return {}, pd.DataFrame()
# 一级分类分布
cid1_dist = df["cid1_name"].value_counts().to_dict()
# 二级分类分布(按一级分类分组)
cid2_dist = df.groupby("cid1_name")["cid2_name"].value_counts().unstack().fillna(0).to_dict()
# 分类销量分析
category_sales = df.groupby(["cid1_name", "cid2_name"]).agg(
total_sales=("sales_count", "sum"),
item_count=("sku_id", "count")
).reset_index()
return {"cid1_dist": cid1_dist, "cid2_dist": cid2_dist}, category_salesdef visualize_category_distribution(cid1_dist: Dict):
"""可视化一级分类分布"""
if not cid1_dist:
return
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
# 饼图:分类占比
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
labels = list(cid1_dist.keys())
sizes = list(cid1_dist.values())
plt.pie(sizes, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%', startangle=90)
plt.title('店铺一级分类商品数量占比')
# 柱状图:分类数量
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
sns.barplot(x=list(cid1_dist.values()), y=labels, palette="viridis")
plt.xlabel('商品数量')
plt.title('各分类商品数量分布')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('category_distribution.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
print("分类分布图表已保存至 category_distribution.png")def analyze_price_distribution(df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""分析价格分布"""
if df.empty:
return pd.DataFrame()
# 价格区间划分
bins = [0, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, float('inf')]
labels = ['0-50元', '50-100元', '100-200元', '200-500元', '500-1000元', '1000元以上']
df["price_range"] = pd.cut(df["price"], bins=bins, labels=labels)
# 按价格区间统计
price_analysis = df.groupby("price_range").agg(
item_count=("sku_id", "count"),
avg_price=("price", "mean"),
total_sales=("sales_count", "sum")
).reset_index()
# 可视化价格分布
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
sns.barplot(x="price_range", y="item_count", data=price_analysis, palette="coolwarm")
plt.title('商品价格区间分布')
plt.xlabel('价格区间')
plt.ylabel('商品数量')
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('price_distribution.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
print("价格分布图表已保存至 price_distribution.png")
return price_analysisdef analyze_top_selling_items(df: pd.DataFrame, top_n: int = 10) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""分析热销商品"""
if df.empty:
return pd.DataFrame()
# 按销量排序
top_selling = df.sort_values("sales_count", ascending=False).head(top_n).copy()
# 可视化热销商品
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 8))
sns.barplot(x="sales_count", y="title", data=top_selling, palette="rocket")
plt.title(f'店铺Top {top_n} 热销商品')
plt.xlabel('30天销量')
plt.ylabel('商品名称')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('top_selling_items.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
print(f"Top {top_n} 热销商品图表已保存至 top_selling_items.png")
return top_selling步骤 6:完整调用与分析示例
python
运行
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 配置应用信息(替换为实际值)
APP_KEY = "your_app_key_here"
APP_SECRET = "your_app_secret_here"
# 目标店铺ID
TARGET_SHOP_ID = "1000000000" # 替换为实际店铺ID
# 初始化API客户端和采集器
shop_api = JdShopItemAPI(APP_KEY, APP_SECRET)
crawler = JdShopItemCrawler(shop_api)
# 1. 采集店铺所有在售商品(最多采集1000件)
print(f"开始采集店铺 {TARGET_SHOP_ID} 的商品数据...")
raw_items_df, stats = crawler.crawl_shop_all_items(
shop_id=TARGET_SHOP_ID,
item_status=1, # 只采集在售商品
max_items=1000 # 限制最大采集数量
)
if raw_items_df.empty:
print("未采集到任何商品数据")
else:
print(f"商品采集完成,共获取 {len(raw_items_df)} 件商品(店铺总商品数: {stats.get('total', 0)})")
# 2. 保存原始数据
raw_items_df.to_csv(f"jd_shop_{TARGET_SHOP_ID}_raw.csv", index=False, encoding="utf-8-sig")
print(f"原始商品数据已保存至 jd_shop_{TARGET_SHOP_ID}_raw.csv")
# 3. 清洗数据
cleaned_df = clean_shop_item_data(raw_items_df)
print(f"数据清洗完成,去重后剩余 {len(cleaned_df)} 件商品")
# 4. 保存清洗后的数据
cleaned_df.to_csv(f"jd_shop_{TARGET_SHOP_ID}_cleaned.csv", index=False, encoding="utf-8-sig")
print(f"清洗后商品数据已保存至 jd_shop_{TARGET_SHOP_ID}_cleaned.csv")
# 5. 品类分析
print("\n开始进行店铺品类分析...")
category_data, category_sales = analyze_shop_category(cleaned_df)
visualize_category_distribution(category_data["cid1_dist"])
# 6. 价格分布分析
print("\n开始进行价格分布分析...")
price_analysis = analyze_price_distribution(cleaned_df)
print("价格区间分析结果:")
print(price_analysis[["price_range", "item_count", "avg_price"]].to_string(index=False))
# 7. 热销商品分析
print("\n开始进行热销商品分析...")
top_selling = analyze_top_selling_items(cleaned_df, top_n=10)
print("Top 10 热销商品:")
print(top_selling[["title", "price", "sales_count", "cid1_name"]].to_string(index=False))
# 8. 折扣分析
discount_analysis = cleaned_df[cleaned_df["discount_rate"].notna()]["discount_rate"].describe()
print("\n商品折扣分析:")
print(f"平均折扣率: {discount_analysis['mean']:.2f}")
print(f"最低折扣率: {discount_analysis['min']:.2f}")
print(f"最高折扣率: {discount_analysis['max']:.2f}")四、缓存与增量更新策略
店铺商品缓存实现
python
运行
import redisimport picklefrom datetime import timedeltaclass CachedJdShopItemAPI(JdShopItemAPI):
def __init__(self, app_key, app_secret, redis_host="localhost", redis_port=6379):
super().__init__(app_key, app_secret)
self.redis = redis.Redis(host=redis_host, port=redis_port, db=0)
# 店铺商品缓存时间(商品信息更新频率较低)
self.cache_ttl = 3600 # 1小时
def get_cache_key(self, shop_id: str, **params) -> str:
"""生成缓存键"""
sorted_params = sorted(params.items())
params_str = "_".join([f"{k}_{v}" for k, v in sorted_params])
return f"jd_shop_items:{shop_id}:{params_str}"
def get_shop_items(self,** kwargs) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""带缓存的店铺商品获取"""
shop_id = kwargs.get("shop_id")
cache_key = self.get_cache_key(shop_id, **kwargs)
# 尝试从缓存获取
cached_data = self.redis.get(cache_key)
if cached_data:
return pickle.loads(cached_data)
# 缓存未命中,调用接口
item_data = super().get_shop_items(** kwargs)
# 存入缓存
if item_data:
self.redis.setex(cache_key, timedelta(seconds=self.cache_ttl), pickle.dumps(item_data))
return item_data增量更新实现
python
运行
def incremental_update_shop_items(crawler: JdShopItemCrawler,
shop_id: str,
last_update_time: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""
增量更新店铺商品(只获取更新时间在last_update_time之后的商品)
:param crawler: 商品采集器
:param shop_id: 店铺ID
:param last_update_time: 上次更新时间(字符串格式)
:return: 新增或更新的商品DataFrame
"""
updated_items = []
page = 1
page_size = 100
has_more = True
# 转换上次更新时间为datetime
try:
last_update_dt = pd.to_datetime(last_update_time)
except:
logging.error("上次更新时间格式错误,返回全量数据")
return crawler.crawl_shop_all_items(shop_id)[0]
while has_more:
# 获取当前页数据
page_data = crawler._get_with_retry(
shop_id=shop_id,
page=page,
page_size=page_size,
item_status=1
)
if not page_data:
break
page_df, page_stats = crawler.parse_shop_items(page_data)
if page_df.empty:
break
# 筛选出更新时间在last_update_time之后的商品
mask = page_df["update_time"] > last_update_dt if mask.any():
updated_items.append(page_df[mask])
# 检查是否还有更多页
total_pages = page_stats.get("total_pages", 1)
has_more = page < total_pages
page += 1
time.sleep(2)
else:
# 本页没有更新的商品,且按更新时间排序的话可以停止
has_more = False
if not updated_items:
return pd.DataFrame()
return pd.concat(updated_items, ignore_index=True)五、常见问题与解决方案
接口调用错误处理
| 错误码 | 错误信息 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 签名错误 | 检查签名生成逻辑,确保参数排序正确,时间戳有效 |
| 1003 | 权限不足 | 确认已申请店铺商品接口权限,企业认证是否通过 |
| 2002 | 店铺不存在 | 验证 shop_id 是否正确,店铺可能已关闭 |
| 429 | 调用频率超限 | 增加请求间隔,使用缓存,错峰采集 |
| 500 | 服务器内部错误 | 实现重试机制,记录详细日志,稍后再试 |
| 110 | IP 不在白名单 | 在京东开放平台添加服务器 IP 到白名单 |
采集效率优化建议
- 分时段采集:python
运行
运行
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completeddef parallel_crawl_shops(shop_ids: list, api: JdShopItemAPI, max_workers: int = 3) -> Dict: """并行采集多个店铺商品""" results = {} crawler = JdShopItemCrawler(api) with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) as executor: futures = { executor.submit(crawler.crawl_shop_all_items, shop_id): shop_id for shop_id in shop_ids } for future in as_completed(futures): shop_id = futures[future] try: df, stats = future.result() results[shop_id] = {"data": df, "stats": stats} print(f"店铺 {shop_id} 采集完成,获取 {len(df)} 件商品") except Exception as e: logging.error(f"店铺 {shop_id} 采集失败: {str(e)}") results[shop_id] = {"error": str(e)} return results
六、合规使用与场景应用
合规使用规范
- 数据使用限制:
不得将采集的店铺商品数据用于恶意竞争
展示店铺商品信息时必须注明来源店铺
不得批量下载商品图片用于其他商业用途
- 调用规范:
单店铺每日采集次数不超过平台限制
采集间隔不得小于 1 秒,避免给服务器造成压力
不得伪造请求来源,需使用真实的 app_key
典型应用场景
- 竞品店铺分析:
采集竞争对手店铺商品数据,分析其品类结构、价格策略和热销商品 - 市场行情监测:
定期采集多个同类店铺商品,监控市场价格波动和新品上架情况 - 供应商评估:
分析店铺商品的品牌分布、价格区间,评估潜在供应商实力 - 店铺运营优化:
对比自身店铺与优秀同行的商品结构差异,优化品类布局
京东店铺商品接口为商家分析提供了全面的数据基础,通过本文介绍的技术方案,开发者可以构建高效的店铺商品采集与分析系统。在实际应用中,应特别注意合规使用,控制采集频率,同时结合缓存和增量更新策略提升性能,让店铺商品数据真正为商业决策提供支持。
def get_optimal_crawl_time() -> bool: """判断是否为最佳采集时间(避开京东接口高峰期)""" hour = time.localtime().tm_hour # 最佳采集时间:凌晨2-6点,接口压力小 return 2 <= hour < 6
- 并行采集控制:python